
Biopolymer Research Centre
Biopolymers are a class of advanced functional materials with the potential to address several future grand challenges that include an aging population and future food shortages. The Biopolymer Research Centre has three main themes: Foods, Drug delivery and Biomaterials, and Extraction and Analysis.
The overall strategy of the Centre is to characterise and understand the fundamental and applied aspects of biopolymer behaviour using a "from source to application approach" whereby biopolymers are extracted, chemically characterised, physically characterised, engineered and potential applications evaluated. We also utilise commercially available biopolymers for new applications in food, pharmaceutical and biomedical technology
Our Mission is to
Implement an interdisciplinary research structure with an international network to maximise the chances of addressing the grand challenges associated with the health and wellbeing of a rapidly rising global population.
Our aims are to
- Provide new solutions to complex problems by crossing the current boundaries of biopolymer research by promoting the cross-fertilisation of ideas for applications between disciplines.
- Deliver high quality training to researchers across pharmaceutical science, food science, biomaterials science and hydrocolloid chemistry in a research environment suitable for mentoring early career researchers.
- Produce high quality researchers with multidisciplinary skills
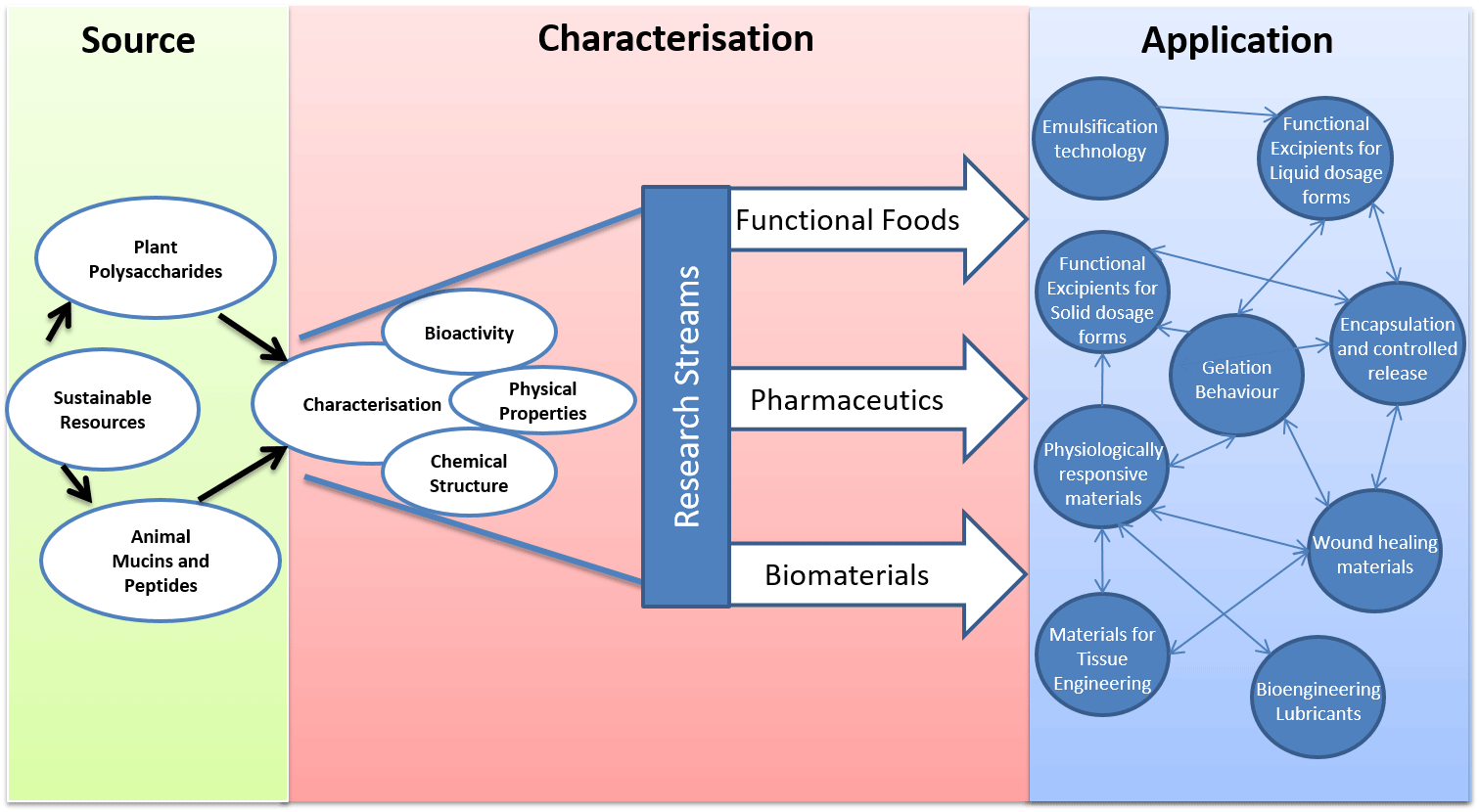
Projects and Research areas
Our research themes and projects

Staff
Meet the team

Impact
Details of the Impact of our work

Facilities
Information about our laboratories and instrumentation

Outputs
Group publications and other outputs

Collaborations
Our academic and industrial collaborations and partnerships

Research Degrees
Opportunities to study with us
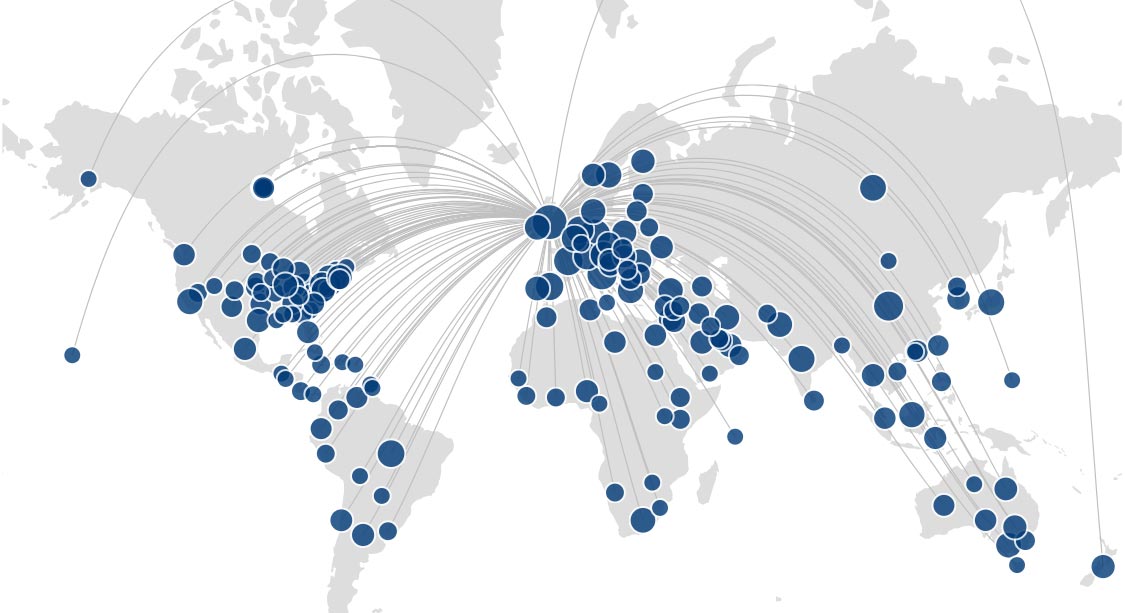
Huddersfield research portal
Search the public portal to discover our researchers, their research expertise and visualize connections among researchers.
Contact Us
If you would like to know more about our areas of expertise or wish to discuss research opportunities with the Biopolymer Research Centre then please contact:
Centre Director: Professor Alan Smith
School of Applied Sciences
University of Huddersfield
Queensgate
Huddersfield
HD1 3DH
Tel: 01484 472305
Email: a.m.smith@hud.ac.uk